Lithium niobate thin films are considered one of the key platforms for next-generation photonic chips due to their excellent electro-optic and nonlinear optical properties as well as extremely low optical loss. However, due to its low electrical conductivity and weak light absorption characteristics, lithium niobate thin films face certain challenges in direct applications in on-chip photodetectors. Associate Professor Xiang Bingshi's team successfully developed several high-performance photodetectors through hetero-integration of two-dimensional materials, providing new technical approaches for the realization of multifunctional lithium niobate thin film photonic chips.
[1] High performance thin film lithium niobate waveguide integrated molybdenum telluride photodetector
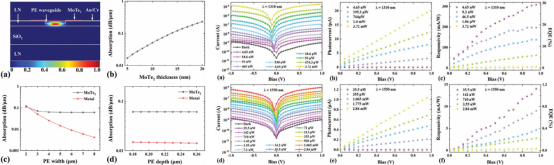
The team proposed a high-performance waveguide-integrated MoTe₂ photodetector based on thin-film lithium niobate. This detector achieves extremely low dark current and an exceptionally high switching ratio. At zero bias and a wavelength of 1310 nm, the dark current is as low as 20 pA, with a switching ratio exceeding 10⁵; at 1 V bias, the dark current is 1.13 nA, the responsivity is 309 mA/W, and the switching ratio reaches 1.8 × 10⁴. The related research findings were published in *Advanced Optical Materials* under the title "Low dark current, high responsivity, and self-powered MoTe₂ photodetector integrated with a thin film lithium niobate waveguide." The first author is Yang Fan, an exchange student from the class of 2022, with Associate Professor Xiang Bingxi as the corresponding author, and Shenzhen Technology University as the primary institution.
[2] Thin film lithium niobate waveguide integrated asymmetric Schottky photodetector
The team innovatively designed an asymmetric Schottky structure, effectively reducing the bandgap width of one side of the material using internal stress in two-dimensional materials, significantly enhancing the self-driven effect of the detector. The detector achieved a self-driven responsivity of 70 mA/W at the optical communication wavelength of 1310 nm, one of the highest levels among waveguide-integrated photodetectors. Additionally, under a bias voltage of-0.5 V, the dark current was as low as 25 pA, with an open-circuit gain ratio as high as 4.1×10⁴. The research findings were published in the international academic journal *Chip*, titled "Self-powered asymmetric Schottky photodetector integrated with thin-film lithium niobate waveguide." The first author is Hu You Tian, a master's student from the class of 2022, with Associate Professor Xiang Bingxi as the corresponding author, and Shenzhen Technology University as the primary institution.

[3] Bidirectional light response tin diselenide hetero-integrated waveguide detector
The team successfully developed a TFLN/SnSe₂ hetero-integrated waveguide detector. This device exhibits extremely high sensitivity for bidirectional light response at different wavelengths and can detect photons with energies below the SnSe₂ bandgap. The highest responsivity of the device reaches 761.78 A/W, making it one of the highest values among two-dimensional material waveguide integrated photodetectors. The related research findings were published in *Advanced Optical Materials* under the title "Ultrasensitive Bidirectional Photoresponse SnSe₂ Photodetector Integration with Thin-Film Lithium Niobate Photonics". The first author is Chen Jiamin, a master's student from the class of 2021, with Associate Professor Xiang Bingxi as the corresponding author, and Shenzhen Technology University as the primary institution.

Full link:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adom.202401822
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chip.2025.100128
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/adom.202301543